The forex market is the largest and most accessible financial market in the world, but although there are many forex investors, few are truly successful ones. Many traders fail for the same reasons that investors fail in other asset classes. In addition, the extreme amount of leverage - the use of borrowed capital to increase the potential return of investments - provided by the market, and the relatively small amounts of margin required when trading currencies, deny traders the opportunity to make numerous low-risk mistakes. Factors specific to trading currencies can cause some traders to expect greater investment returns than the market can consistently offer, or to take more risk than they would when trading in other markets.
Forex Market Trading Hazards
Certain mistakes can keep traders from achieving their investment goals. Following are some of the common pitfalls that can plague forex traders:
Managing Leverage
Although these mistakes can afflict all types of traders and investors, issues inherent in the forex market can significantly increase trading risks. The significant amount of financial leverage afforded forex traders presents additional risk that must be managed.
Leverage provides traders with an opportunity to enhance returns. But leverage and the commensurate financial risk is a double-edged sword that amplifies the downside as much as it adds to potential gains. The forex market allows traders to leverage their accounts as much as 400:1, which can lead to massive trading gains in some cases - and account for crippling losses in others. The market allows traders to use vast amounts of financial risk, but in many cases it is in a trader's best interest to limit the amount of leverage used.
Most professional traders use about 2:1 leverage by trading one standard lot ($100,000) for every $50,000 in their trading accounts. This coincides with one mini lot ($10,000) for every $5,000 and one micro lot ($1,000) for every $500 of account value. The amount of leverage available comes from the amount of margin that brokers require for each trade. Margin is simply a good faith deposit that you make to insulate the broker from potential losses on a trade. The bank pools the margin deposits into one very large margin deposit that it uses to make trades with the interbank market. Anyone that has ever had a trade go horribly wrong knows about the dreadful margin call, where brokers demand additional cash deposits; if they don't get them, they will sell the position at a loss to mitigate further losses or recoup their capital.
Many forex brokers require various amounts of margin, which translates into the following popular leverage ratios:
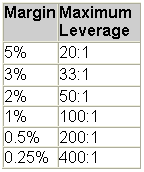
ason many forex traders fail is that they are undercapitalized in relation to the size of the trades they make. It is either greed or the prospect of controlling vast amounts of money with only a small amount of capital that coerces forex traders to take on such huge and fragile financial risk. For example, at a 100:1 leverage (a rather common leverage ratio), it only takes a -1% change in price to result in a 100% loss. And every loss, even the small ones taken by being stopped out of a trade early, only exacerbates the problem by reducing the overall account balance and further increasing the leverage ratio.
Not only does leverage magnify losses, but it also increases transaction costs as a percent of account value. For example, if a trader with a mini account of $500 uses 100:1 leverage by buying five mini lots ($10,000) of a currency pair with a five-pip spread, the trader also incurs $25 in transaction costs [(1/pip x 5 pip spread) x 5 lots]. Before the trade even begins, he or she has to catch up, since the $25 in transaction costs represents 5% of the account value. The higher the leverage, the higher the transaction costs as a percentage of account value, and these costs increase as the account value drops.
While the forex market is expected to be less volatile in the long term than the equity market, it is obvious that the inability to withstand periodic losses and the negative effect of those periodic losses through high leverage levels are a disaster waiting to happen. These issues are compounded by the fact that the forex market contains a significant level of macroeconomic and political risks that can create short-term pricing inefficiencies and play havoc with the value of certain currency pairs.
In Summary
Many of the factors that cause forex traders to fail are similar to those that plague investors in other asset classes. The simplest way to avoid some of these pitfalls is to build a relationship with other successful forex traders who can teach you the trading disciplines required by the asset class, including the risk and money management rules required to trade the forex market. Only then will you be able to plan appropriately and trade with the return expectations that keep you from taking excessive risk for the potential benefits.
While understanding the macroeconomic, technical and fundamental analysis necessary for trading forex is as important as the requisite trading psychology, one of the largest factors that separates success from failure is a trader's ability to manage a trading account. The keys to account management include making sure to be sufficiently capitalized, using appropriate trade sizing and limiting financial risk by using smart leverage levels.
Robert Stammers can be contacted at the CFA Institute and you can also Follow @robertstammers on Twitter
Forex Market Trading Hazards
Certain mistakes can keep traders from achieving their investment goals. Following are some of the common pitfalls that can plague forex traders:
- Not Maintaining Trading Discipline
The largest mistake any trader can make is to let emotions control trading decisions. Becoming a successful forex trader means achieving a few big wins while suffering many smaller losses. Experiencing many consecutive losses is difficult to handle emotionally and can test a trader's patience and confidence. Trying to beat the market or giving in to fear and greed can lead to cutting winners short and letting losing trades run out of control. Conquering emotion is achieved by trading within a well-constructed trading plan that assists in maintaining trading discipline.
- Trading Without a Plan
Whether one trades forex or any other asset class, the first step in achieving success is to create and follow a trading plan. "Failing to plan is planning to fail" is an adage that holds true for any type of trading. The successful trader works within a documented plan that includes risk management rules and specifies the expected return on investment (ROI). Adhering to a strategic trading plan can help investors evade some of the most common trading pitfalls; if you don't have a plan, you're selling yourself short in what you can accomplish in the forex market.
- Failing to Adapt to the Market
Before the market even opens, you should create a plan for every trade. Conducting scenario analysis and planning the moves and countermoves for every potential market situation can significantly reduce the risk of large, unexpected losses. As the market changes, it presents new opportunities and risks. No panacea or foolproof "system" can persistently prevail over the long term. The most successful traders adapt to market changes and modify their strategies to conform to them. Successful traders plan for low probability events and are rarely surprised if they occur. Through an education and adaptation process, they stay ahead of the pack and continuously find new and creative ways to profit from the evolving market.
- Learning Through Trial and Error
Without a doubt, the most expensive way to learn to trade the currency markets is through trial and error. Discovering the appropriate trading strategies by learning from your mistakes is not an efficient way to trade any market. Since forex is considerably different from the equity market, the probability of new traders sustaining account-crippling losses is high. The most efficient way to become a successful currency trader is to access the experience of successful traders. This can be done through a formal trading education or through a mentor relationship with someone who has a notable track record. One of the best ways to perfect your skills is to shadow a successful trader, especially when you add hours of practice on your own.
- Having Unrealistic Expectations
No matter what anyone says, trading forex is not a get-rich-quick scheme. Becoming proficient enough to accumulate profits is not a sprint - it's a marathon. Success requires recurrent efforts to master the strategies involved. Swinging for the fences or trying to force the market to provide abnormal returns usually results in traders risking more capital than warranted by the potential profits. Foregoing trade discipline to gamble on unrealistic gains means abandoning risk and money management rules that are designed to prevent market remorse.
- Poor Risk and Money Management
Traders should put as much focus on risk management as they do on developing strategy. Some naive individuals will trade without protection and abstain from using stop losses and similar tactics in fear of being stopped out too early. At any given time, successful traders know exactly how much of their investment capital is at risk and are satisfied that it is appropriate in relation to the projected benefits. As the trading account becomes larger, capital preservation becomes more important. Diversification among trading strategies and currency pairs, in concert with the appropriate position sizing, can insulate a trading account from unfixable losses. Superior traders will segment their accounts into separate risk/return tranches, where only a small portion of their account is used for high-risk trades and the balance is traded conservatively. This type of asset allocation strategy will also ensure that low-probability events and broken trades cannot devastate one's trading account.
Managing Leverage
Although these mistakes can afflict all types of traders and investors, issues inherent in the forex market can significantly increase trading risks. The significant amount of financial leverage afforded forex traders presents additional risk that must be managed.
Leverage provides traders with an opportunity to enhance returns. But leverage and the commensurate financial risk is a double-edged sword that amplifies the downside as much as it adds to potential gains. The forex market allows traders to leverage their accounts as much as 400:1, which can lead to massive trading gains in some cases - and account for crippling losses in others. The market allows traders to use vast amounts of financial risk, but in many cases it is in a trader's best interest to limit the amount of leverage used.
Most professional traders use about 2:1 leverage by trading one standard lot ($100,000) for every $50,000 in their trading accounts. This coincides with one mini lot ($10,000) for every $5,000 and one micro lot ($1,000) for every $500 of account value. The amount of leverage available comes from the amount of margin that brokers require for each trade. Margin is simply a good faith deposit that you make to insulate the broker from potential losses on a trade. The bank pools the margin deposits into one very large margin deposit that it uses to make trades with the interbank market. Anyone that has ever had a trade go horribly wrong knows about the dreadful margin call, where brokers demand additional cash deposits; if they don't get them, they will sell the position at a loss to mitigate further losses or recoup their capital.
Many forex brokers require various amounts of margin, which translates into the following popular leverage ratios:
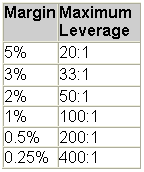
ason many forex traders fail is that they are undercapitalized in relation to the size of the trades they make. It is either greed or the prospect of controlling vast amounts of money with only a small amount of capital that coerces forex traders to take on such huge and fragile financial risk. For example, at a 100:1 leverage (a rather common leverage ratio), it only takes a -1% change in price to result in a 100% loss. And every loss, even the small ones taken by being stopped out of a trade early, only exacerbates the problem by reducing the overall account balance and further increasing the leverage ratio.
Not only does leverage magnify losses, but it also increases transaction costs as a percent of account value. For example, if a trader with a mini account of $500 uses 100:1 leverage by buying five mini lots ($10,000) of a currency pair with a five-pip spread, the trader also incurs $25 in transaction costs [(1/pip x 5 pip spread) x 5 lots]. Before the trade even begins, he or she has to catch up, since the $25 in transaction costs represents 5% of the account value. The higher the leverage, the higher the transaction costs as a percentage of account value, and these costs increase as the account value drops.
While the forex market is expected to be less volatile in the long term than the equity market, it is obvious that the inability to withstand periodic losses and the negative effect of those periodic losses through high leverage levels are a disaster waiting to happen. These issues are compounded by the fact that the forex market contains a significant level of macroeconomic and political risks that can create short-term pricing inefficiencies and play havoc with the value of certain currency pairs.
In Summary
Many of the factors that cause forex traders to fail are similar to those that plague investors in other asset classes. The simplest way to avoid some of these pitfalls is to build a relationship with other successful forex traders who can teach you the trading disciplines required by the asset class, including the risk and money management rules required to trade the forex market. Only then will you be able to plan appropriately and trade with the return expectations that keep you from taking excessive risk for the potential benefits.
While understanding the macroeconomic, technical and fundamental analysis necessary for trading forex is as important as the requisite trading psychology, one of the largest factors that separates success from failure is a trader's ability to manage a trading account. The keys to account management include making sure to be sufficiently capitalized, using appropriate trade sizing and limiting financial risk by using smart leverage levels.
Robert Stammers can be contacted at the CFA Institute and you can also Follow @robertstammers on Twitter
Last edited by a moderator:
